

Shandong Science ›› 2025, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 13-27.doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.20240103
• Overview of Ecological Protection Technologies in the Yellow River Basin • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yongfeng1( ), YU Jingyuan2, ZHANG Hao3
), YU Jingyuan2, ZHANG Hao3
Received:2024-08-26
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2025-04-16
CLC Number:
WANG Yongfeng, YU Jingyuan, ZHANG Hao. Review of the sources, distribution, and health risks of bisphenol compounds in environmental media in China[J].Shandong Science, 2025, 38(2): 13-27.
Table 1
Structures and characteristics of typical bisphenol compounds"
| 中文名 | 英文缩写 | CAS号 | 分子式 | 分子结构 | log Kow | 溶解度/(mg·L-1) | 主要用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 双酚A | BPA | 80-05-7 | C15H16O2 | 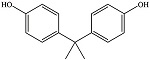 | 3.32 | 71 | 制造聚碳酸酯塑 料和环氧树脂 |
| 双酚B | BPB | 77-40-7 | C16H18O2 | 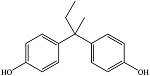 | 4.13 | 44 | 生产某些塑料和树脂 |
| 双酚E | BPE | 2081-08-5 | C14H14O2 |  | 3.19 | 99 | 生产某些特殊树脂和涂料 |
| 双酚F | BPF | 620-92-8 | C13H12O2 |  | 2.91 | 200 | 环氧树脂和其他热固性 树脂的硬化剂 |
| 双酚P | BPP | 2167-51-3 | C24H26O2 | 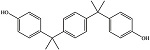 | 6.25 | 0.59 | 生产某些塑料和树脂 |
| 双酚S | BPS | 80-09-1 | C12H10O4S | 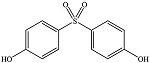 | 1.65 | 350 | 生产聚碳酸酯塑料 和环氧树脂 |
| 双酚Z | BPZ | 843-55-0 | C18H20O2 | 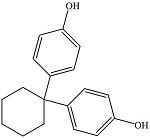 | 5.00 | 14 | 生产某些高性能 树脂和塑料 |
| 双酚AF | BPAF | 1478-61-1 | C15H10F6O2 | 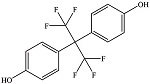 | 4.47 | 21 | 生产高性能聚合物 和特种涂料 |
| 双酚AP | BPAP | 1571-75-1 | C20H18O2 | 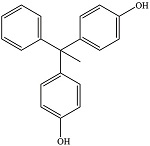 | 4.86 | 13 | 生产某些特种塑料和树脂 |
| 四溴双酚A | TBBPA | 79-94-7 | C15H12Br4O2 | 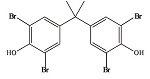 | 4.50 | 1.26 | 提高材料的阻燃性能 |
Table 2
Concentrations of typical bisphenol pollutants in surface water"
| 取样地点 | 污染物质量浓度a/(ng·L-1) | 数据来源 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | BPS | BPF | BPAF | BPB | BPAP | BPZ | BPP | BPE | TBBPA | |||
| 长江三角洲 | 太湖 | 28~560 (97) | 4.5~1 600 (120) | N.D.~1 600 (140) | 0.7~23 (8.2) | N.D.~28 (5.8) | 1.0~15 (4.8) | N.D.~17 (3.9) | [ | |||
| 太湖 | 19~68 (26) | 4.1~160 (16) | 26~720 (78) | 110~140 (110) | 18~46 (20) | 1.6~2.9 (1.9) | ~17 (17) | [ | ||||
| 骆马湖 | 49~110 (86) | N.D.~94 (21) | 3.5~14 (6.8) | 12~84 (17) | 6.4~23 (8.8) | 4.3~56 (11) | 2.7~45 (7.7) | [ | ||||
| 长江 | 0.18~14.9 (1.39) | [ | ||||||||||
| 秦淮河 | 120~554 (253) | 2.24~73.3 (39.2) | N.D.~4.76 (2.2) | 1.5~16.2 (5.1) | N.D. | [ | ||||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 珠江 (旱季) | 45.8~1 840 (200) | 2.16~56.9 (14) | 6.54~34.4 (12.2) | N.D.~1.95 (0.31) | N.D.~0.53 (<0.3) | N.D.~0.89 (<0.25) | [ | ||||
| 珠江 (雨季) | 118~1 770 (471) | 16.6~103 (44.5) | 2.16~16.2 (8.94) | N.D.~0.96 (0.35) | N.D.~0.97 (<0.3) | N.D.~0.89 (<0.25) | [ | |||||
| 东江 (旱季) | 19~712 (165) | 0.07~31 (1.7) | 0.98~255 (25.2) | 0.62~6.59 (4.2) | N.D.~0.44 (<0.3) | N.D.~0.52 (<0.25) | [ | |||||
| 东江 (雨季) | 23.7~2 180 (406) | 0.07~133 (12.7) | 0.24~19 (6.22) | N.D.~2.58 (1.01) | N.D.~1.09 (<0.3) | N.D.~1.93 (<0.25) | [ | |||||
| 流溪河 | 75.6~7 480 (922) | 19.9~65 600 (3 720) | N.D.~474 (82.8) | [ | ||||||||
| 珠江口 | 9.48~173 (24.6) | 1.6~59.8 (10.3) | 2.37~282 (35) | 0.4~3.59 (0.7) | 0.17~13.1 (1.51) | 0.27~1.53 (0.41) | [ | |||||
| 珠江 | 13.9~126 (36.9) | N.D.~124.4 (38.7) | N.D.~13.1 (8.3) | N.D.~123.1 (18.3) | N.D.~8.8 (4.6) | N.D.~8.9 (0.65) | N.D.~8 (0.5) | N.D.~2.8 (0.2) | N.D.~2.7 (1.5) | [ | ||
Table 3
Concentrations of typical bisphenol pollutants in sediments"
| 取样地点 | 污染物质量分数a/(ng·g-1) | 数据来源 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | BPS | BPF | BPAF | BPB | BPAP | BPZ | BPP | BPE | TBBPA | |||||||||||||
| 长三角区域 | 太湖 | 1.1~200 (20) | 0.31~31 (4.1) | 0.54~20 (4.7) | N.D.~0.27 (0.03) | 1.1~6.6 (2.2) | 0.68~1.2 (0.76) | 0.61~1.1 (0.69) | [ | |||||||||||||
| 太湖 | 3.6~270 (32) | 0.22~47 (3.1) | 3.0~9.5 (12) | 11~19 (12) | 1.8~4.0 (2.1) | 0.16~0.68 (0.29) | 1.7~2.6 (2.0) | [ | ||||||||||||||
| 骆马湖 | 6.2~9.3 (8.0) | N.D.~0.25 (0.12) | 0.68~1.4 (1.0) | N.D.~1.5 (0.94) | N.D.~0.83 (0.36) | 0.43~0.62 (0.49) | 0.26~0.38 (0.33) | [ | ||||||||||||||
| 秦淮河 (非汛期) | 3.17~137 (14.6) | N.D.~1.05 (0.805) | N.D.~14.9 (3.0) | N.D. | N.D.~3.41 (0.177) | N.D.~0.672 (0.129) | [ | |||||||||||||||
| 秦淮河 (汛期) | 1.80~54.5 (12.2) | N.D.~0.144 (0.007) | N.D.~11.8 (2.88) | N.D. | N.D.~3.39 (0.44) | N.D.~1.42 (0.252) | [ | |||||||||||||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 珠江(旱季) | 118~689 (406) | N.D.~5.6 (1.14) | 26.7~341 (123) | N.D.~4.4 (2.19) | N.D. | N.D.~1.81 (<0.34) | [ | ||||||||||||||
| 珠江(雨季) | 145~723 (388) | N.D.~2.35 (<0.55) | 16~194 (85.7) | N.D.~3.51 (1.34) | N.D. | N.D.~2.78 (0.43) | [ | |||||||||||||||
| 东江(旱季) | 26.6~1 860 (217) | 0.27~0.59 (0.33) | 51.4~1 390 (389) | 0.25~1.77 (0.59) | N.D.~2.32 (<0.95) | N.D.~1.16 (<0.34) | [ | |||||||||||||||
| 东江(雨季) | 29.8~1 970 (346) | 0.27~0.78 (<0.55) | 40.9~1 040 (345) | 0.25~1.42 (0.82) | N.D.~1.49 (<0.95) | N.D.~1.52 (<0.34) | [ | |||||||||||||||
| 流溪河 | 0.11~359 (98.3) | 0.06~45.4 (7.25) | 0.02~36.4 (11.1) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 近海区域 | 北部沿海 (渤海和黄海) | N.D.~116 (1.87) | N.D.~0.389 (0.144) | N.D.~4.37 (1.06) | N.D.~1.89 (0.153) | [ | ||||||||||||||||
| 辽河口 | N.D.~68.2 (16.7) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 北部湾 | 0.56~5.22 (1.58) | N.D.~0.19 (0.05) | N.D. | 0.08~0.66 (0.21) | N.D.~0.06 (0.01) | [ | ||||||||||||||||
Table 4
Concentrations of typical bisphenol pollutants in soil"
| 取样地点 | 污染物质量分数a/ (ng·g-1) | 数据来源 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | BPS | BPF | BPAF | BPB | BPAP | BPZ | BPP | BPE | TBBPA | ||||||||||||
| 城镇区域 | 农田(全国14 个不同区域) | 0.2~166 (11.48) | N.D.~0.6 (0.11) b | N.D.~212.9 (14.45) | N.D. | N.D.~0.5 (0.14) | N.D.~3 (0.51) | N.D.~0.2 (0.01) | N.D.~78.2 (5.32) | N.D.~1.1 (0.24) | [ | ||||||||||
| 城市(全国15 个不同区域) | N.D.~38.7 (4.51) | N.D.~0.3 (0.05) | N.D.~3.7 (0.84) | N.D.~0.2 (0.07) | N.D.~0.3 (0.05) | N.D.~0.5 (0.29) | N.D. | N.D.~6.1 (0.62) | 0.4~0.7 (0.53) | [ | |||||||||||
| 农田(张家港) | N.D.~173.75 (14.79) | N.D.~151.53 (7.92) | N.D.~68.49 (4.89) | N.D.~21.63 (1.05) | N.D.~0.76 (0.08) | N.D.~0.7 (0.02) | N.D.~31.56 (0.44) | [ | |||||||||||||
| 成都 | 26.3~553 (113) | 0.308~6.67 (1.27) | N.D.~26.5 (2.29) | 0.227~7.01 (1.39) | N.D.~13.1 (1.08) | N.D.~18.4 (2.18) | N.D. | N.D.~3.5 (0.37) | N.D. | [ | |||||||||||
| 污染场地周边 | 电子垃圾拆 解区域(台州) | N.D.~12.3 (4.59) | 0.03~8.35 (2.04) | 0.08~8.81 (2.63) | [ | ||||||||||||||||
| 电子垃圾拆解 工业园(贵屿) | 366~108 000 (2 350) | 82.6~98 300 (10 800) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 电子垃圾拆解工 业园周边(贵屿) | N.D.~4 060 (491) | N.D.~8 490 (293) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 电线回收工 业园(清远) | N.D.~25 900 (4 820) | 25.2~1 230 (270) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 电线回收工业 园周边(清远) | N.D.~2 400 (396) | 1.02~766 (131) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 化工园区 (寿光) | N.D.~35.30 (3.83) | N.D.~387 (44.60) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 小清河(寿光) | 0.19~18.70 (4.61) | 0.26~83.70 (17.90) | [ | ||||||||||||||||||
| [1] | EFSA CEF Panel. Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs[J]. EFSA Journal, 2015, 13(1): 3978. DOI:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3978. |
| [2] | EFSA CEP Panel, LAMBRÉ C, BARAT BAVIERA J M, et al. Re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs[J]. EFSA Journal, 2023, 21(4): e06857. DOI:10.2903/j.efsa.2023.6857. |
| [3] | CHEN D, KANNAN K, TAN H L, et al. Bisphenolanalogues other than BPA: Environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity:A review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(11): 5438-5453. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.5b05387. |
| [4] | QADEER A, KIRSTEN K L, AJMAL Z, et al. Alternative plasticizers as emerging global environmental and health threat: Another regrettable substitution?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(3): 1482-1488. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.1c08365. |
| [5] | DUEÑAS-MORENO J, MORA A, CERVANTES-AVILÉS P, et al. Groundwater contamination pathways of phthalates and bisphenol A: Origin, characteristics, transport, and fate - A review[J]. Environment International, 2022, 170: 107550. DOI:10.1016/j.envint.2022.107550. |
| [6] | ZHANG S, FAN Y F, QIAN X, et al. Occurrence, source apportionment and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues in river sediments in areas with different land use patterns[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 359: 121041. DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121041. |
| [7] |
SUN Q, WANG Y W, LI Y, et al. Fate and mass balance of bisphenol analogues in wastewater treatment plants in Xiamen City, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225: 542-549. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.018.
pmid: 28318793 |
| [8] | HUANG Z, ZHAO J L, YANG Y Y, et al. Occurrence, mass loads and risks of bisphenol analogues in the Pearl River Delta region, South China: Urban rainfall runoff as a potential source for receiving rivers[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 114361. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114361. |
| [9] |
SONG S J, SONG M Y, ZENG L Z, et al. Occurrence and profiles of bisphenol analogues in municipal sewage sludge in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 186: 14-19. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.023.
pmid: 24355443 |
| [10] |
PANG L, YANG H Q, LV L N, et al. Occurrence and estrogenic potency of bisphenol analogs in sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Central China[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2019, 77(3): 461-470. DOI:10.1007/s00244-019-00663-4.
pmid: 31422434 |
| [11] | LIAO M X, GAN Z W, SUN W Y, et al. Spatial distribution, source identification, and potential risks of 14 bisphenol analogues in soil under different land uses in the megacity of Chengdu, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 352: 124064. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124064. |
| [12] |
CHEN W P, XU J, LU S D, et al. Fates and transport of PPCPs in soil receiving reclaimed water irrigation[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(10): 2621-2630. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.088.
pmid: 24148973 |
| [13] | AKRAM R, IQBAL R, HUSSAIN R, et al. Evaluation of Oxidative stress, antioxidant enzymes and genotoxic potential of bisphenol A in fresh water bighead carp (Aristichthys nobils) fish at low concentrations[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115896. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115896. |
| [14] | SANTOS J D S, PONTES M D S, DE SOUZA M B, et al. Toxicity of bisphenol A (BPA) and its analogues BPF and BPS on the free-floating macrophyte Salvinia biloba[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 343: 140235. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140235. |
| [15] |
STANISZEWSKA M, NEHRING I, MUDRAK-CEGIOŁKA S. Changes of concentrations and possibility of accumulation of bisphenol A and alkylphenols, depending on biomass and composition, in zooplankton of the Southern Baltic (Gulf of Gdansk)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 213: 489-501. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.004.
pmid: 26970874 |
| [16] | LI D, CHEN H X, BI R, et al. Individual and binary mixture effects of bisphenol A and lignin-derived bisphenol in Daphnia magna under chronic exposure[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 779-786. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.022. |
| [17] |
YAN Z Y, LIU Y H, YAN K, et al. Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: Occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 318-328. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.010.
pmid: 28601665 |
| [18] | LIU Y H, ZHANG S H, SONG N H, et al. Occurrence, distribution and sources of bisphenol analogues in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): Implications for ecological and human health risk[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599: 1090-1098. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.069. |
| [19] | WANG H, TANG Z, LIU Z H, et al. Occurrence, spatial distribution, and main source identification of ten bisphenol analogues in the dry season of the Pearl River, South China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(18): 27352-27365. DOI:10.1007/s11356-021-17647-4. |
| [20] |
ZHAO X, QIU W H, ZHENG Y, et al. Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues, parabens and their metabolites in the Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 180: 43-52. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.083.
pmid: 31063942 |
| [21] | GAO Y, XIAO S K, WU Q, et al. Bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: Occurrence, partitioning and risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159445. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159445. |
| [22] |
HUANG C, WU L H, LIU G Q, et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of eight endocrine-disrupting chemicals in urban river water and sediments of South China[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 75(2): 224-235. DOI:10.1007/s00244-018-0527-9.
pmid: 29725723 |
| [23] | ZHENG C Y, LIU J C, REN J H, et al. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues in the surface water from a water diversion project in Nanjing, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(18): 3296. DOI:10.3390/ijerph16183296. |
| [24] |
GONG J, DUAN D D, YANG Y, et al. Seasonal variation and partitioning of endocrine disrupting chemicals in waters and sediments of the Pearl River system, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 735-741. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.015.
pmid: 27431692 |
| [25] | WANG Y L, ZHANG X T, GUO F, et al. Estimating the temporal and spatial distribution and threats of bisphenol A in temperate lakes using machine learning models[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2024, 269: 115750. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115750. |
| [26] |
WAN Y J, XIA W, YANG S Y, et al. Spatial distribution of bisphenol S in surface water and human serum from Yangtze River watershed, China: Implications for exposure through drinking water[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 199: 595-602. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.040.
pmid: 29459349 |
| [27] | QIN Y H, LIU J C, HAN L, et al. Medium distribution, source characteristics and ecological risk of bisphenol compounds in agricultural environment[J]. Emerging Contaminants, 2024, 10(2): 100292. DOI:10.1016/j.emcon.2023.100292. |
| [28] | IM J, LÖFFLER F E. Fate of bisphenol A in terrestrial and aquatic environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(16): 8403-8416. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.6b00877. |
| [29] |
LIAO C Y, SHI J B, WANG X Y, et al. Occurrence and distribution of parabens and bisphenols in sediment from northern Chinese coastal areas[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 253: 759-767. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.076.
pmid: 31344538 |
| [30] |
YUAN X T, YANG X L, ZHANG A G, et al. Distribution, potential sources and ecological risks of two persistent organic pollutants in the intertidal sediment at the Shuangtaizi Estuary, Bohai Sea of China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 419-427. DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.058.
pmid: 27745742 |
| [31] |
STAPLES C, FRIEDERICH U, HALL T, et al. Estimating potential risks to terrestrial invertebrates and plants exposed to bisphenol A in soil amended with activated sludge biosolids[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2010, 29(2): 467-475. DOI:10.1002/etc.49.
pmid: 20821466 |
| [32] |
VERDÚ I, TRIGO D, MARTÍNEZ-GUITARTE J L, et al. Bisphenol A in artificial soil: Effects on growth, reproduction and immunity in earthworms[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 190: 287-295. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.122.
pmid: 28992482 |
| [33] |
KIM D, KWAK J I, AN Y J. Effects of bisphenol A in soil on growth, photosynthesis activity, and genistein levels in crop plants (Vigna radiata)[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 875-882. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.146.
pmid: 30114736 |
| [34] | XU Y W, HU A L, LI Y R, et al. Determination and occurrence of bisphenol A and thirteen structural analogs in soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 277: 130232. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130232. |
| [35] | WEI D L, YUAN K J, AI F X, et al. Occurrence, spatial distributions, and temporal trends of bisphenol analogues in an E-waste dismantling area: Implications for risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 867: 161498. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161498. |
| [36] | GE X, MA S T, HUO Y P, et al. Mixed bromine/chlorine transformation products of tetrabromobisphenol A: Potential specific molecular markers in e-waste dismantling areas[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 423: 127126. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127126. |
| [37] | CAO P, ZHONG H N, QIU K, et al. Exposure to bisphenol A and its substitutes, bisphenol F and bisphenol S from canned foods and beverages on Chinese market[J]. Food Control, 2021, 120: 107502. DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107502. |
| [38] | WANG H, LIU Z H, TANG Z, et al. Bisphenol analogues in Chinese bottled water: Quantification and potential risk analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 713: 136583. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136583. |
| [39] |
YANG Y J, YANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Assessment of bisphenol A alternatives in paper products from the Chinese market and their dermal exposure in the general population[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 244: 238-246. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.049.
pmid: 30342365 |
| [40] | DING T D, CAI M, WU C C, et al. Distribution profiles of bisphenols in school supplies and implications for human exposure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 849: 157938. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157938. |
| [41] | LI A J, KANNAN K. Elevated concentrations of bisphenols, benzophenones, and antimicrobials in pantyhose collected from six countries[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(18): 10812-10819. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.8b03129. |
| [42] | ZHANG H, QUAN Q, ZHANG M Y, et al. Occurrence of bisphenol A and its alternatives in paired urine and indoor dust from Chinese university students: Implications for human exposure[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 247: 125987. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125987. |
| [43] |
LIU Y H, YAN Z Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Urinary levels, composition profile and cumulative risk of bisphenols in preschool-aged children from Nanjing suburb, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 172: 444-450. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.002.
pmid: 30735977 |
| [44] | GAO C Z, HE H H, QIU W H, et al. Oxidative stress, endocrine disturbance, and immune interference in humans showed relationships to serum bisphenol concentrations in a dense industrial area[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(3): 1953-1963. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.0c07587. |
| [45] | JIN H B, XIE J H, MAO L L, et al. Bisphenol analogue concentrations in human breast milk and their associations with postnatal infant growth[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 259: 113779. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113779. |
| [46] | SHEN J, KANG Q M, MAO Y C, et al. Urinary bisphenol A concentration is correlated with poorer oocyte retrieval and embryo implantation outcomes in patients with tubal factor infertility undergoing in vitro fertilisation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 187: 109816. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109816. |
| [47] |
WANG B, ZHOU W, ZHU W T, et al. Associations of female exposure to bisphenol A with fecundability: Evidence from a preconception cohort study[J]. Environment International, 2018, 117: 139-145. DOI:10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.003.
pmid: 29751163 |
| [48] | RADWAN M, WIELGOMAS B, DZIEWIRSKA E, et al. Urinary bisphenol A levels and male fertility[J]. American Journal of Men’s Health, 2018, 12(6): 2144-2151. DOI:10.1177/1557988318799163. |
| [49] | CATENZA C J, FAROOQ A, SHUBEAR N S, et al. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 268: 129273. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129273. |
| [50] | HUI L, LI H Y, LU G, et al. Low dose of bisphenol A modulates ovarian cancer gene expression profile and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition via canonical Wnt pathway[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2018, 164(2): 527-538. DOI:10.1093/toxsci/kfy107. |
| [51] |
HUANG W, ZHAO C, ZHONG H, et al. Bisphenol S induced epigenetic and transcriptional changes in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 697-703. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.084.
pmid: 30616060 |
| [52] | LEI B L, SUN S, XU J, et al. Low-concentration BPAF- and BPF-induced cell biological effects are mediated by ROS in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(4): 3200-3208. DOI:10.1007/s11356-017-9709-7. |
| [53] |
DUAN Y S, YAO Y M, WANG B, et al. Association of urinary concentrations of bisphenols with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 1719-1726. DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.093.
pmid: 30408859 |
| [54] | LIU B Y, LEHMLER H J, SUN Y B, et al. Association of bisphenol A and its substitutes, bisphenol F and bisphenol S, with obesity in United States children and adolescents[J]. Diabetes & Metabolism Journal, 2019, 43(1): 59-75. DOI:10.4093/dmj.2018.0045. |
| [55] | 刘惠楠, 孙振东, 刘倩, 等. 合成酚类化合物的脂代谢干扰效应与致肥胖作用[J]. 色谱, 2024, 42(2): 131-141. DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12018. |
| [56] | XU Y Q, NIE J, LU C H, et al. Effects and mechanisms of bisphenols exposure on neurodegenerative diseases risk: A systemic review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 919: 170670. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170670. |
| [57] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 4806.7—2023食品安全国家标准食品接触用塑料材料及制品[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2024. |
| [1] | XU Jianping, ZHANG Shilei, CHEN Chen, ZHU Jianjun, GUO Yupu. Carbon sequestration effect of aggregate spray-seeding technology in ecological restoration of damaged slopes [J]. Shandong Science, 2025, 38(5): 115-122. |
| [2] | MA Jinyan, ZHAO Rusong. Current status of contamination of environmental and food samples with pharmaceutical and personal care products and sample pretreatment analytical techniques [J]. Shandong Science, 2025, 38(2): 28-40. |
|
||

Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits third parties to freely share (i.e., copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) and adapt (i.e., remix, transform, or build upon the material) the articles published in this journal, provided that appropriate credit is given, a link to the license is provided, and any changes made are indicated. The material may not be used for commercial purposes. For details of the CC BY-NC 4.0 license, please visit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0